 Mathematics
MathematicsRiemann Sums
A Riemann sum, one of the many things named after Bernhard Riemann, is a finite sum that can be used to approximate an integral by partitioning the area under a curve into rectangles. This problem will explore the process of approximating area under a curve using Riemann sums.
Definition
Consider the following function:
We need the area under this function between and
. In other words, we need to approximate the following integral:
We can plot the function to get a better idea of what it looks like:
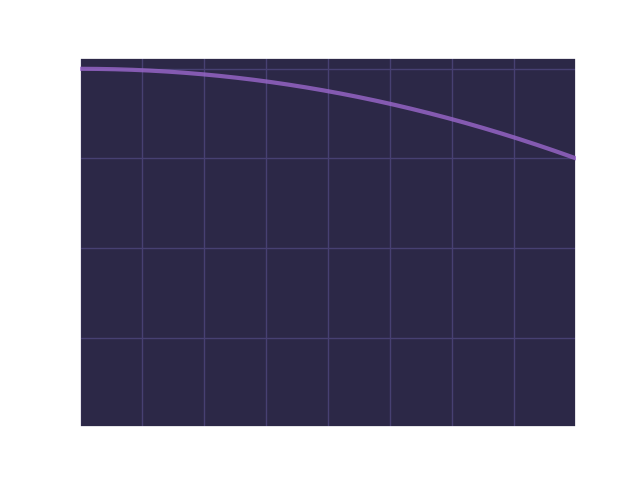
If we manually compute the definite integral, we get recurring. Let's see how good our approximations are!
Left Riemann Sum
We can partition this function into 4 evenly spaced sections of width 0.5 and draw rectangles such that the top-left corner of the rectangle touches the function's curve:
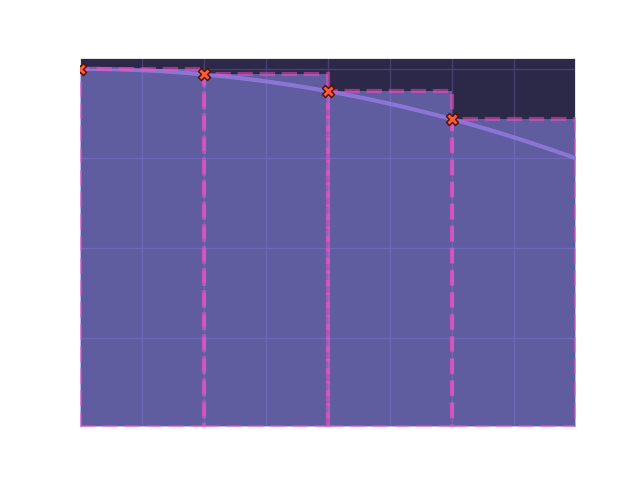
Now all we need to do is find the total area of all these rectangles:
Close! But we overshot. Can we do better?
Right Riemann Sum
Now we can draw rectangles such that the top-right corner of the rectangle touches the function's curve:
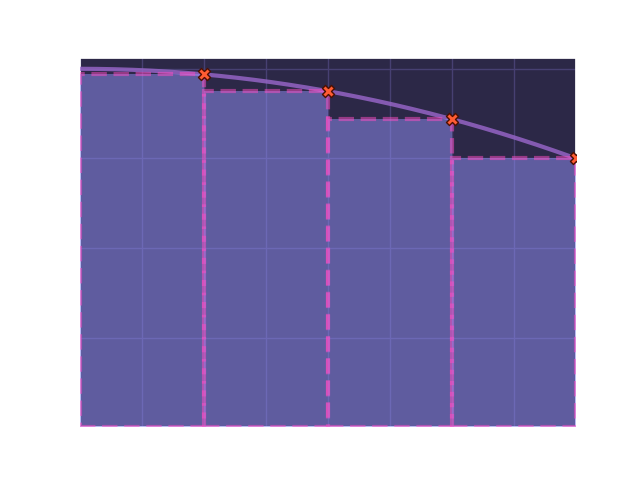
Once again, we need to do is find the total area of all these rectangles:
Close again! But this time we undershot. Let's try one more time.
Mid-point Riemann Sum
We can draw rectangles such that the mid-point of the rectangle's top touches the function's curve:
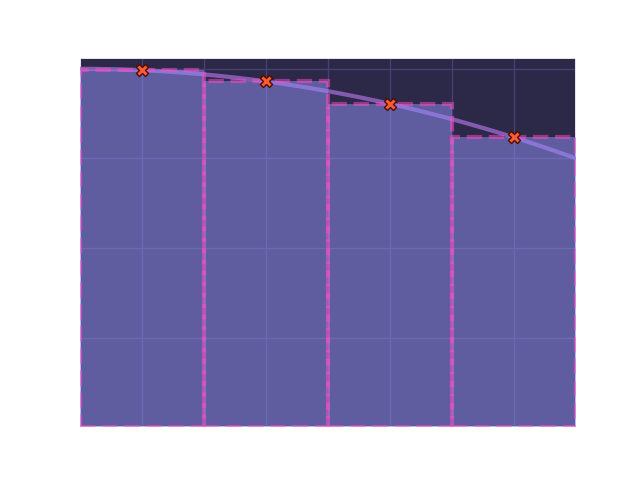
Finally, we need to do is find the total area of all these rectangles:
That's our best approximation so far!
Exercise
Write a program using NumPy that approximates the area under a curve using Rieman sums. Complete the compute_left_riemann_sum(), compute_right_riemann_sum(), and compute_midpoint_riemann_sum() methods:
compute_left_riemann_sum()takes in a functionf, a pair of limitslimits, and the number of partitionsn, and computes the Riemann sum using rectangles that touch the curve using their top-left cornerscompute_right_riemann_sum()takes in a functionf, a pair of limitslimits, and the number of partitionsn, and computes the Riemann sum using rectangles that touch the curve using their top-right cornerscompute_midpoint_riemann_sum()takes in a functionf, a pair of limitslimits, and the number of partitionsn, and computes the Riemann sum using rectangles that touch the curve using the mid-point of their tops
Sample Test Cases
Test Case 1
Input:
[
[-1, 0, 16],
[0, 2],
4
]
Output:
left_riemann_sum = 30.25
right_riemann_sum = 28.25
midpoint_riemann_sum = 29.375
Test Case 2
Input:
[
[1,3,2],
[-2, 2],
4
]
Output:
left_riemann_sum = 8.0
right_riemann_sum = 20.0
midpoint_riemann_sum = 13.0
