 Machine Learning
Machine LearningActivation Functions
One of the most crucial roles in neural network architecture is played by activation functions. Activation functions are simple transformations that are applied to the outputs of individual neurons in the network, introducing non-linearity to it and enabling it to learn more complex patterns. For this exercise, we will explore and implement different types of activation functions.
An activation function takes in an matrix of values
and transforms it into
. Note that the sizes of matrices
and
are the same.
In this exercise, we will explore 5 of the most common activation functions.
Step Function
The step function is defined by:
The following is a plot of the step function:
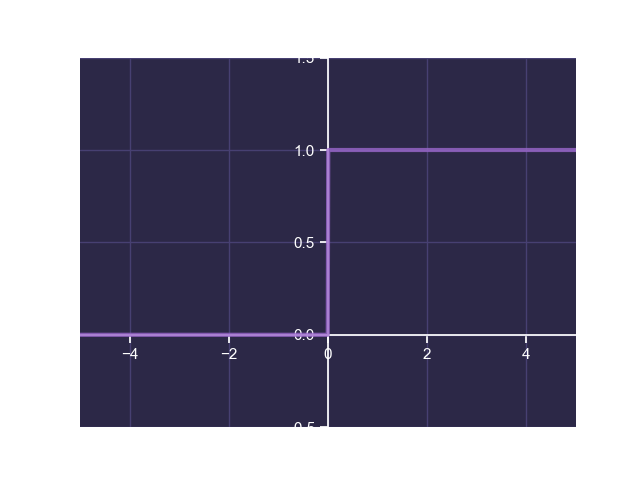
The step function transforms a continuous input to a binary output and is often used as the final layer in a binary classification network. However, because it's derivative is undefined at and is equal to
everywhere else, it is not very useful for learning in neural networks.
Sigmoid Function
The sigmoid function is defined by:
The following is a plot of the sigmoid function:
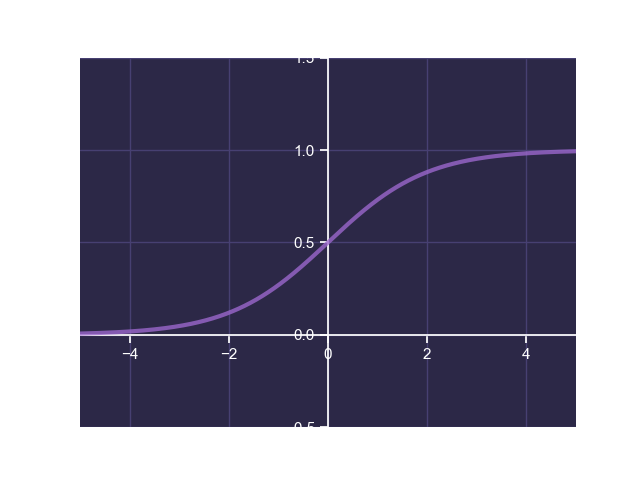
The sigmoid function transforms a continuous input to a continuous output between 0 and 1. This property is extremely useful for neural networks tasked with classification. Additionally, the sigmoid function is differentiable for all values of , making it suitable for learning algorithms.
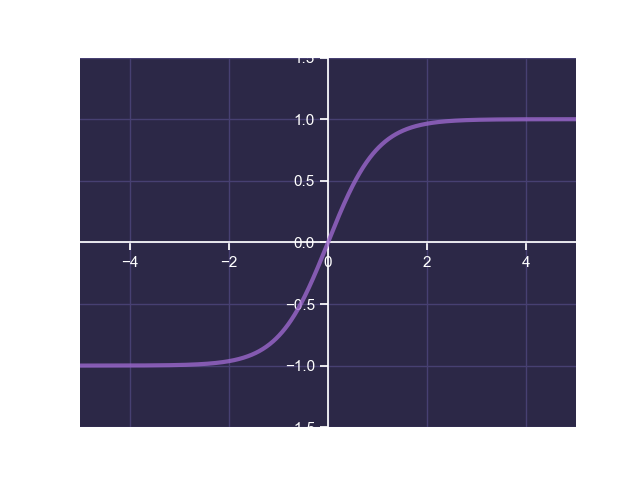
Hyperbolic Tangent
The hyperbolic tangent is defined by:
The following is a plot of hyperbolic tangent:
Hyperbolic tangent transforms a continuous input to a continuous output between -1 and 1. Once again this is useful for neural networks tasked with classification. Like the sigmoid function, the hyperbolic tangent is also differentiable for all values of , making it suitable for learning algorithms.
Rectified Linear Unit
The rectified linear unit (ReLU) function is defined by:
The following is a plot of ReLU:
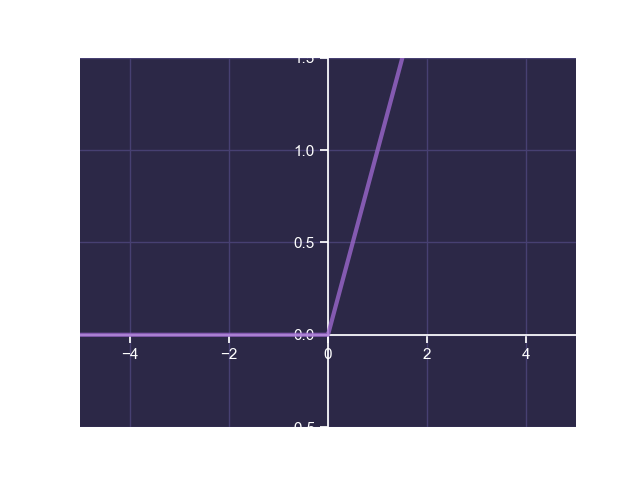
ReLU transforms a continuous input to a continuous positive output. It is also useful for neural networks and can often be used to avoid the vanishing gradient problem observed with the sigmoid function.
Leaky Rectified Linear Unit
The leaky rectified linear unit function is defined by:
The following is a plot of leaky ReLU:
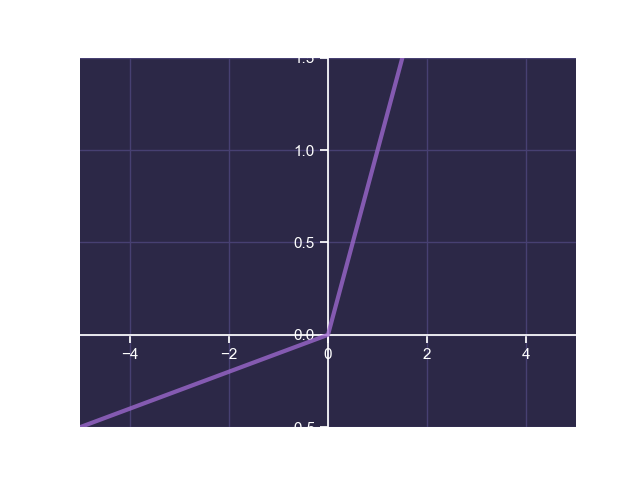
Leaky ReLU transforms a continuous input to a continuous output, where the gradient of the output when the input is negative is given by the parameter . Unlike ReLU, leaky ReLU does not output
when the input is zero. This helps avoid the dying ReLU problem that is often observed with ReLU.
Softmax
The entry of the softmax function's output is defined as follows:
where is the
entry of matrix
.
The following is a visualization of how softmax works:
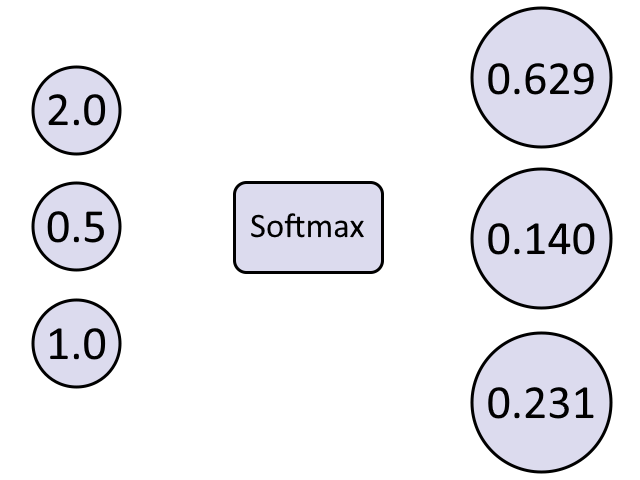
Note that the softmax function is the only one in this exercise that cannot be applied individually to each element in and must be applied collectively to all the elements in
. Softmax transforms a set of continuous input values to a set of corresponding continuous probability values between 0 and 1. This is often useful for neural networks in multi-class classification problems.
Exercise
Write a program using NumPy that performs the activation functions on a given input. Complete the sigmoid(), tanh(), relu(), leaky_relu(), and softmax() methods:
step()takes in a multi-dimensional input arrayX, performs the step function on each element and returns the result as an array of the same shape. This has already been implemented for you.sigmoid()takes in a multi-dimensional input arrayX, performs the sigmoid function on each element and returns the result as an array of the same shapetanh()takes in a multi-dimensional input arrayX, performs the hyperbolic tangent function on each element and returns the result as an array of the same shaperelu()takes in a multi-dimensional input arrayX, performs ReLU on each element and returns the result as an array of the same shapeleaky_relu()takes in a multi-dimensional input arrayX, performs leaky ReLU on each element and returns the result as an array of the same shapesoftmax()takes in a multi-dimensional input arrayX, performs the softmax function and returns the result as an array of the same shape
Sample Test Cases
Test Case 1
Input:
[
[2, 0.5, 1],
0.25
]
Output:
sigmoid = [0.881, 0.622, 0.731]
tanh = [0.964, 0.462, 0.762]
relu = [2, 0.5, 1]
leaky_relu = [2, 0.5, 1]
softmax = [0.629, 0.14, 0.231]
Test Case 2
Input:
[
[-1, 2],
0.1
]
Output:
sigmoid = [0.269, 0.881]
tanh = [-0.762, 0.964]
relu = [0, 2]
leaky_relu = [-0.1, 2]
softmax = [0.047, 0.953]
